Understanding Health Informatics Core Competencies - Part 1

By Johannes Thye, MA, Faculty of Business Management and Social Sciences, University of Applied Sciences Osnabrück, Germany; Consortium member of the EU*US eHealth Work Project
The term core competence is a rather vague concept that should be classified. Core competencies can be understood as a broadly specialised system of skills, abilities or knowledge necessary to achieve a specific goal. Core competencies also include behaviour that includes emotional, social and cognitive aspects. It is evident that it is not only about knowledge, but also about abilities, skills and behaviour. Ultimately, it is a combination of cognitive, motivational, moral and social skills that align to fulfil requirements, solve tasks and problems or achieve goals through the necessary knowledge and actions.
With regard to health informatics, these core competencies are not simply the transfer of knowledge about the use of a specific application, but rather the development of knowledge in order to use information technology (IT) sensibly and to give IT a meaning. In healthcare, there are also specific core competencies related to medical or nursing activities. Furthermore, the treatment of patients is interprofessional, in this sense, informatics core competencies in healthcare basically cover different disciplines and professions. Thus, health IT is interprofessional by nature and must be reflected in education and training. Especially core competencies such as communication and leadership are of great importance for successful interprofessional cooperation.
What Kind of Core Competencies Exist?
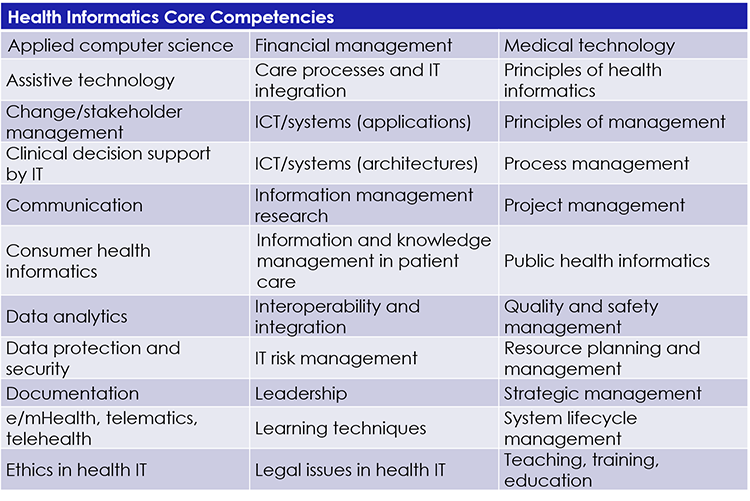
Core competencies can be divided into different domains such as IT principles, ethical and legal issues, systems life cycle management, medical technology or management. These can be subdivided into a technology, application or management focus, and the addition of interpersonal skills can also be derived. In a more detailed subdivision of management, the core competences of the individual areas such as strategic management, project management or the principles of management thus derived. Furthermore, core competencies can also be defined according to different levels, such as the Bloom taxonomy. The following table shows in summary the health informatics core competencies developed and derived for the TIGER International Competency Synthesis Project’s Recommendation Framework 2.0.
Interprofessional Competencies
As mentioned above, health IT as well as the treatment of patients is interprofessional by nature. There are always differences in the need for digital skills in the various health professions, yet there is also a large common overlap between the professions.
Professions working in direct patient care (such as physicians, nurses or therapists) share many common competencies such as documentation, quality management or information and knowledge management. Other professions such as IT engineers and chief information officers or IT engineers and executives also have a large overlap in their competencies. In particular, communication and leadership are of special importance to all occupational groups in healthcare in order to support interprofessional cooperation.
The aim is to integrate health informatics core competencies into the traditional training, curricula and courseware (at all educational levels) and to prepare the teachers as gatekeepers and multipliers in education. Finally, the common core competencies can also be used for collaborative education between the professional groups.
Posts You’d Might Like

Understanding Health Informatics Core Competencies - Part 1
Global health informatics is a growing multidisciplinary field that deals in applications of technology to improve [global] healthcare systems and outcomes.

Understanding Health Informatics Core Competencies - Part 2
The move towards digital transformation in healthcare requires users who are competent and ethical in the use of devices, information systems, data management and technology mediated interaction.

Understanding Health Informatics Core Competencies - Part 3
The need for competent health informaticists and data scientists is growing exponentially. Additionally, the amount of data produced by the healthcare industry is expected to grow exponentially, creating opportunities a plenty in many areas.


Share Now